Embark on a journey through the realm of securing health data with cloud technology, where challenges meet solutions and risks are mitigated with best practices. Discover the essential strategies that safeguard sensitive information in the digital age.
Delve into the complexities of encryption, access control, compliance, and disaster recovery, as we explore the intricate landscape of health data security in the cloud.
Overview of Health Data Security in Cloud Technology
Securing health data in the cloud is crucial to protect sensitive information and maintain patient privacy. As healthcare organizations increasingly adopt cloud technology for storing and managing data, it is important to understand the key challenges, risks, and best practices involved in ensuring the security of health information.
The Importance of Securing Health Data in the Cloud
Health data contains highly sensitive information, including medical history, treatment plans, and personal details. Unauthorized access to this data can lead to identity theft, fraud, and compromised patient care. Securing health data in the cloud helps prevent data breaches and ensures compliance with healthcare regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Key Challenges in Protecting Health Data in a Cloud Environment
- Lack of control over data: Healthcare organizations may face challenges in managing and monitoring data security when data is stored in the cloud.
- Compliance requirements: Ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards while using cloud services can be complex.
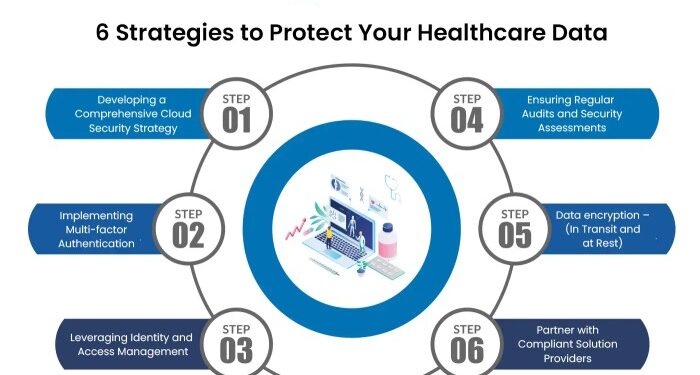
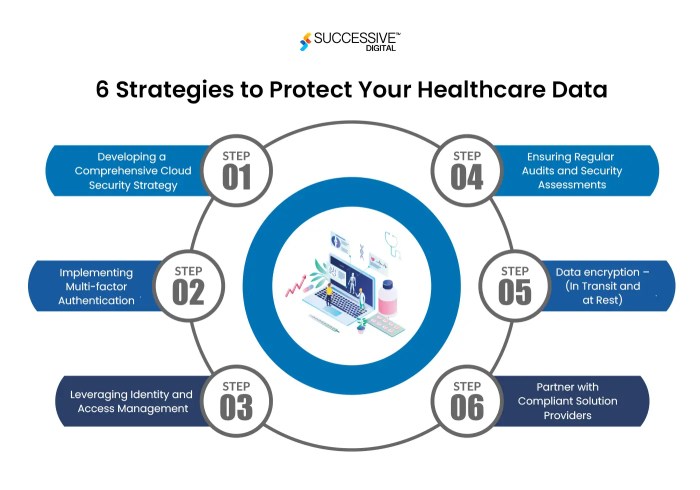
- Data encryption: Encrypting health data in transit and at rest is essential but may be challenging to implement effectively.
Risks Associated with Storing Health Information in the Cloud
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive health data can result in financial loss, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
- Data loss: Inadequate backup and recovery processes in the cloud can lead to permanent loss of critical health information.
- Vendor vulnerabilities: Cloud service providers may be susceptible to security vulnerabilities that could compromise the confidentiality and integrity of health data.
Comparison of Traditional Data Security Measures with Cloud-Based Security Practices
- Traditional data security measures often involve on-premises infrastructure, firewalls, and access controls, while cloud-based security practices rely on encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure APIs.
- Cloud security offers scalability and flexibility compared to traditional security measures, allowing healthcare organizations to adapt to changing data storage needs more easily.
Encryption and Access Control
Encryption plays a crucial role in protecting health data stored in the cloud. It ensures that even if unauthorized users gain access to the data, they cannot read or decipher it. Access control, on the other hand, regulates who can view, edit, or delete the health data, adding an extra layer of security.
Encryption for Data at Rest and Data in Transit
Encryption for data at rest involves securing data that is stored in the cloud servers. This is typically achieved by encrypting the data before it is stored and decrypting it when it needs to be accessed. Best practices for implementing encryption for data at rest include using strong encryption algorithms, regularly updating encryption keys, and limiting access to the encryption keys to authorized personnel only.Encryption for data in transit focuses on securing data as it is transferred between the user's device and the cloud servers.
This is commonly done using protocols like SSL/TLS to establish secure connections. Best practices for implementing encryption for data in transit include using secure communication protocols, encrypting sensitive data before transmission, and regularly monitoring and updating encryption protocols to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Access Control Mechanisms in Cloud Environments
Access control mechanisms in cloud environments help ensure that only authorized individuals can access health data. Some examples of access control mechanisms used in cloud environments include:
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Assigning roles to users and granting permissions based on those roles.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing the data.
Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
Granting access based on specific attributes of the user, data, or environment.
Privileged access management (PAM)
Monitoring and controlling privileged users' access to sensitive data.Implementing a combination of these access control mechanisms can significantly enhance the security of health data stored in the cloud.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks is crucial when it comes to securing health data in the cloud. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in severe consequences for organizations.
Common Regulatory Frameworks
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient data. It requires the implementation of safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic protected health information (ePHI).
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR is a regulation in the European Union that focuses on data protection and privacy. It imposes strict requirements on how organizations handle personal data, including health information.
Importance of Compliance
- Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR helps protect patient privacy and prevent data breaches.
- Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal penalties, and damage to an organization's reputation.
Role of Cloud Technology
- Cloud technology offers advanced security features such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, which can help organizations meet regulatory requirements.
- Cloud service providers often have compliance certifications that demonstrate adherence to industry standards, providing assurance to organizations handling health data.
Demonstrating Compliance
- Conduct regular risk assessments and audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Implement strong access controls, encryption mechanisms, and data backup procedures to protect health data in the cloud.
- Maintain documentation of security policies, procedures, and incident response plans to demonstrate a proactive approach to data security.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Ensuring proper data backup and disaster recovery procedures are essential in safeguarding health data stored in the cloud. In the event of data loss or system failures, having backups and recovery plans in place can help minimize downtime and prevent potential data breaches.
Importance of Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Implementing robust backup and recovery strategies is crucial for protecting sensitive health data from various risks such as accidental deletions, cyberattacks, hardware failures, and natural disasters. Regular backups ensure that critical data is securely stored and can be restored quickly in case of emergencies.
Best Practices for Implementing Backup and Recovery Strategies in the Cloud
- Regularly schedule automated backups to ensure data is consistently backed up without manual intervention.
- Encrypt backup data to maintain confidentiality and integrity during storage and transmission.
- Test recovery procedures periodically to verify the effectiveness of backup systems and ensure data can be restored successfully.
- Implement a multi-tiered backup strategy with off-site storage to protect against localized incidents.
Differences Between Data Backups and Disaster Recovery Plans
Data backups focus on creating copies of data to prevent permanent loss, while disaster recovery plans involve comprehensive strategies to resume operations after a catastrophic event. Backups are essential for recovering specific data, while disaster recovery plans encompass broader strategies for restoring entire systems and applications.
Examples of Cloud-Based Backup Solutions for Health Data
- Amazon S3 Glacier: Offers low-cost archival storage with flexible retrieval options for long-term data retention.
- Microsoft Azure Backup: Provides automated backup services with built-in security features for protecting health data in the cloud.
- Google Cloud Storage Nearline: Enables quick access to data for disaster recovery purposes while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the paramount importance of implementing robust security measures for health data in cloud technology cannot be overstated. By adhering to best practices and regulatory standards, organizations can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information, ultimately fostering trust and reliability in the digital healthcare ecosystem.
Helpful Answers
How can encryption protect health data in the cloud?
Encryption scrambles data to make it unreadable without the correct decryption key, ensuring confidentiality and security.
What are examples of access control mechanisms used in cloud environments?
Access control mechanisms like role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) help restrict unauthorized access to health data.
Why is compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR crucial for securing health data?
Compliance ensures that organizations follow strict guidelines to protect sensitive health information and avoid penalties for data breaches.
What is the difference between data backups and disaster recovery plans?
Data backups involve making copies of data for safekeeping, while disaster recovery plans focus on restoring operations after a catastrophic event.
How can organizations demonstrate compliance with health data security standards?
Organizations can showcase compliance through audits, documentation of security measures, and adherence to regulatory requirements.