What Is Health Information Technology and Why It Matters in 2025 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. As we delve into the world of healthcare technology, we uncover the transformative power it holds for the future of medicine and patient care.
With advancements on the horizon and innovations that promise to revolutionize the way we approach healthcare, the significance of health information technology cannot be overstated. Let's embark on this journey together to explore the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
What Is Health Information Technology

Health Information Technology (HIT) refers to the use of technology in managing healthcare information. It involves the electronic storage, retrieval, and sharing of patient health information to improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Key Components of Health Information Technology
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Digital versions of patients' paper charts, containing medical history, diagnoses, medications, treatment plans, immunization dates, allergies, radiology images, and laboratory test results.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE): Allows healthcare professionals to appropriately access and securely share patient information electronically.
- Telemedicine: The use of telecommunications technology to provide remote clinical services to patients without an in-person visit.
Role of Health Information Technology in Healthcare
Health Information Technology plays a crucial role in improving communication, streamlining processes, reducing medical errors, and enhancing patient outcomes in healthcare settings. It enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions and deliver personalized care based on accurate and up-to-date patient information.
Use of Health Information Technology to Improve Patient Care and Outcomes
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Allows healthcare providers to track patients' vital signs and symptoms remotely, enabling early intervention and proactive care management.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): Assist healthcare providers in making clinical decisions by providing evidence-based guidance and alerts for potential issues or interactions.
- Personal Health Records (PHR): Empower patients to manage and access their health information, promoting active participation in their healthcare.
Examples of Common Health Information Technologies
- Patient Portals: Online platforms that allow patients to access their health records, schedule appointments, communicate with healthcare providers, and refill prescriptions.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): Store and manage medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans digitally for easy access and sharing among healthcare professionals.
- Electronic Prescribing (e-prescribing): Enables healthcare providers to electronically send prescriptions to pharmacies, reducing medication errors and improving medication adherence.
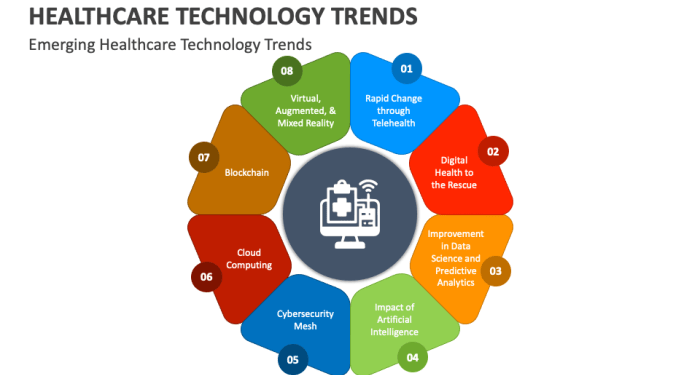
Importance of Health Information Technology in 2025
Health Information Technology (HIT) is poised to play a crucial role in the future of healthcare, particularly in 2025. The advancements and innovations in HIT are expected to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered, improving patient outcomes, enhancing efficiency, and reducing healthcare costs.
Advancements and Innovations in Health Information Technology
- Enhanced Interoperability: By 2025, HIT systems are projected to achieve seamless interoperability, allowing for the secure exchange of patient data across different healthcare settings. This will facilitate better coordination of care and enable healthcare providers to make more informed decisions.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into HIT systems will enable predictive analytics, personalized medicine, and early disease detection. This will lead to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans for patients.
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: With the advancement of telemedicine technologies, patients will have greater access to healthcare services remotely. Remote monitoring devices will allow for continuous tracking of patient health metrics, leading to proactive interventions and improved chronic disease management.
Addressing Current Healthcare Challenges
- Reducing Medical Errors: The implementation of advanced HIT systems with decision support tools can help in reducing medical errors, improving patient safety, and enhancing the quality of care delivery.
- Improving Population Health Management: By leveraging data analytics and population health management tools, healthcare organizations can identify at-risk populations, implement preventive interventions, and ultimately improve the health outcomes of communities.
Benefits of Implementing Advanced Health Information Technologies
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Advanced HIT systems streamline administrative processes, reduce duplication of tests, and eliminate paperwork, leading to cost savings for healthcare organizations and improved operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Through patient portals, telehealth services, and mobile health apps, advanced HIT technologies empower patients to actively participate in their care, leading to better health outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
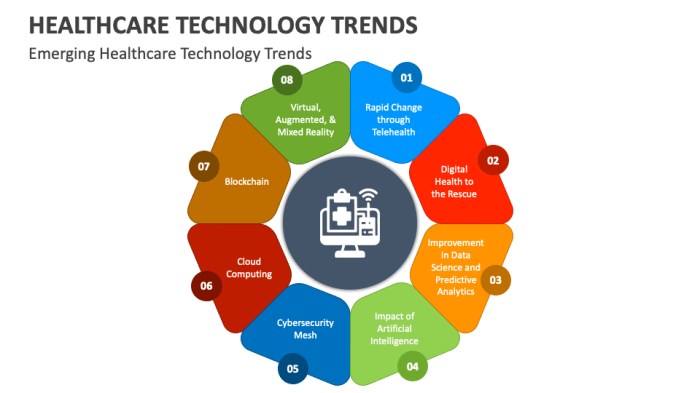
Emerging Trends in Health Information Technology
Health Information Technology is constantly evolving, driven by the need for more efficient, accurate, and accessible healthcare services. Let's explore some of the emerging trends shaping the field in 2025.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling predictive analytics, personalized medicine, and improved decision-making processes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends, helping healthcare providers deliver more targeted and effective treatments.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
- Telemedicine allows patients to consult with healthcare professionals remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving access to care, especially in rural or underserved areas.
- Remote monitoring devices, such as wearables and IoT sensors, enable continuous tracking of patient health metrics, providing real-time data to healthcare providers for proactive interventions and personalized treatment plans.
Data Analytics and Interoperability
Data analytics plays a crucial role in extracting actionable insights from vast amounts of healthcare data, driving informed decision-making and quality improvement initiatives. Interoperability, on the other hand, ensures seamless exchange of health information between different systems and providers, enhancing care coordination and patient outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting Health Information Technology
Implementing health information technology in healthcare organizations comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. From technical issues to privacy concerns, there are several factors that need to be addressed for successful adoption.
Common Challenges Faced by Healthcare Organizations
- Lack of interoperability between different systems, leading to difficulty in sharing patient information seamlessly.
- Resistance to change among healthcare professionals who may be accustomed to traditional paper-based methods.
- Initial high costs of implementing health information technology systems and the need for ongoing maintenance and upgrades.
- Potential disruptions to workflow during the transition period, affecting productivity and patient care.
Privacy and Security Concerns
- Protecting sensitive patient data from cyber threats and unauthorized access is crucial in health information technology systems.
- Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA is essential to ensure patient confidentiality and data security.
- Implementing robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to safeguard patient information from breaches.
Importance of Training and Education
- Providing comprehensive training to healthcare professionals on how to use health information technology effectively can enhance adoption and usage.
- Ongoing education on best practices and updates in technology is necessary to keep healthcare staff informed and skilled.
- Encouraging a culture of continuous learning and improvement to ensure that healthcare professionals are proficient in utilizing technology for patient care.
Strategies for Overcoming Barriers
- Engage stakeholders early in the planning process to ensure buy-in and support for the implementation of health information technology.
- Collaborate with IT experts and vendors to customize solutions that meet the specific needs of the healthcare organization.
- Gradual implementation and phased approaches can help mitigate disruptions and allow for smoother transitions.
- Evaluate and address concerns proactively, seeking feedback from users to continuously improve the system and address any issues that arise.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the landscape of healthcare technology is evolving rapidly, and the role of health information technology is pivotal in shaping this future. As we look towards 2025 and beyond, the potential for growth and improvement in patient outcomes is immense.
Embracing these advancements will not only address current healthcare challenges but also pave the way for a healthier tomorrow.
Popular Questions
What are the key components of health information technology?
Health information technology includes electronic health records, telemedicine platforms, health information exchange systems, and clinical decision support tools.
How can health information technology address current healthcare challenges?
By improving data analytics, enhancing interoperability, and facilitating remote monitoring, health information technology can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and ultimately enhance patient care.
What advancements can we expect in health information technology by 2025?
Anticipated advancements include increased use of artificial intelligence for diagnostics, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and wider adoption of telehealth solutions to reach remote populations.
What are some common challenges in adopting health information technology?
Common challenges include initial costs of implementation, resistance to change from healthcare professionals, and ensuring data privacy and security in electronic health records.
Why is training and education important for healthcare professionals using health information technology?
Proper training ensures that healthcare professionals can effectively use health information technology tools, leading to better integration, reduced errors, and improved patient outcomes.